Purification and Formulation
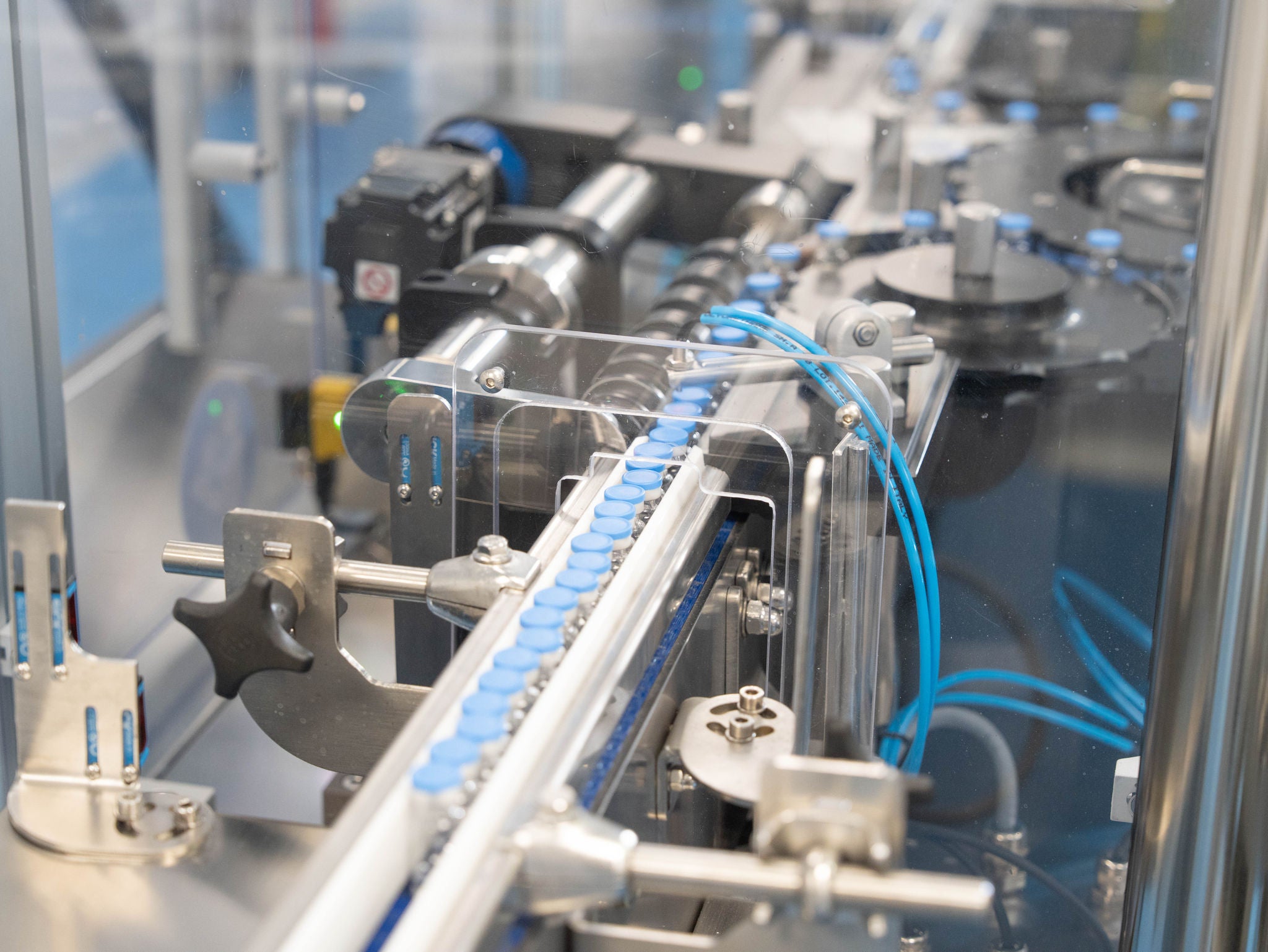
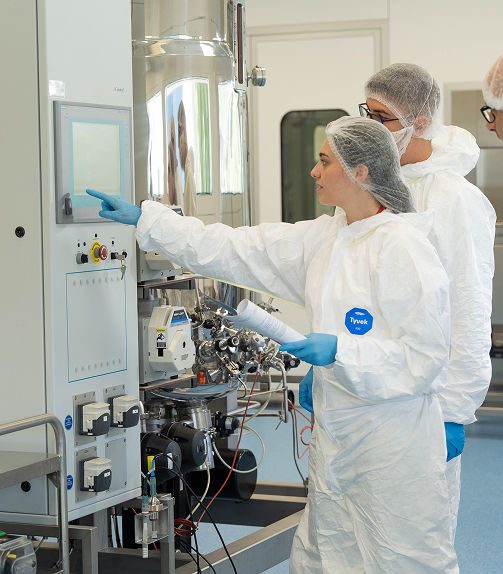
In the Downstream phase, the active ingredient is carefully purified using advanced separation technologies—such as chromatography and filtration—to ensure its quality, safety, and efficacy.
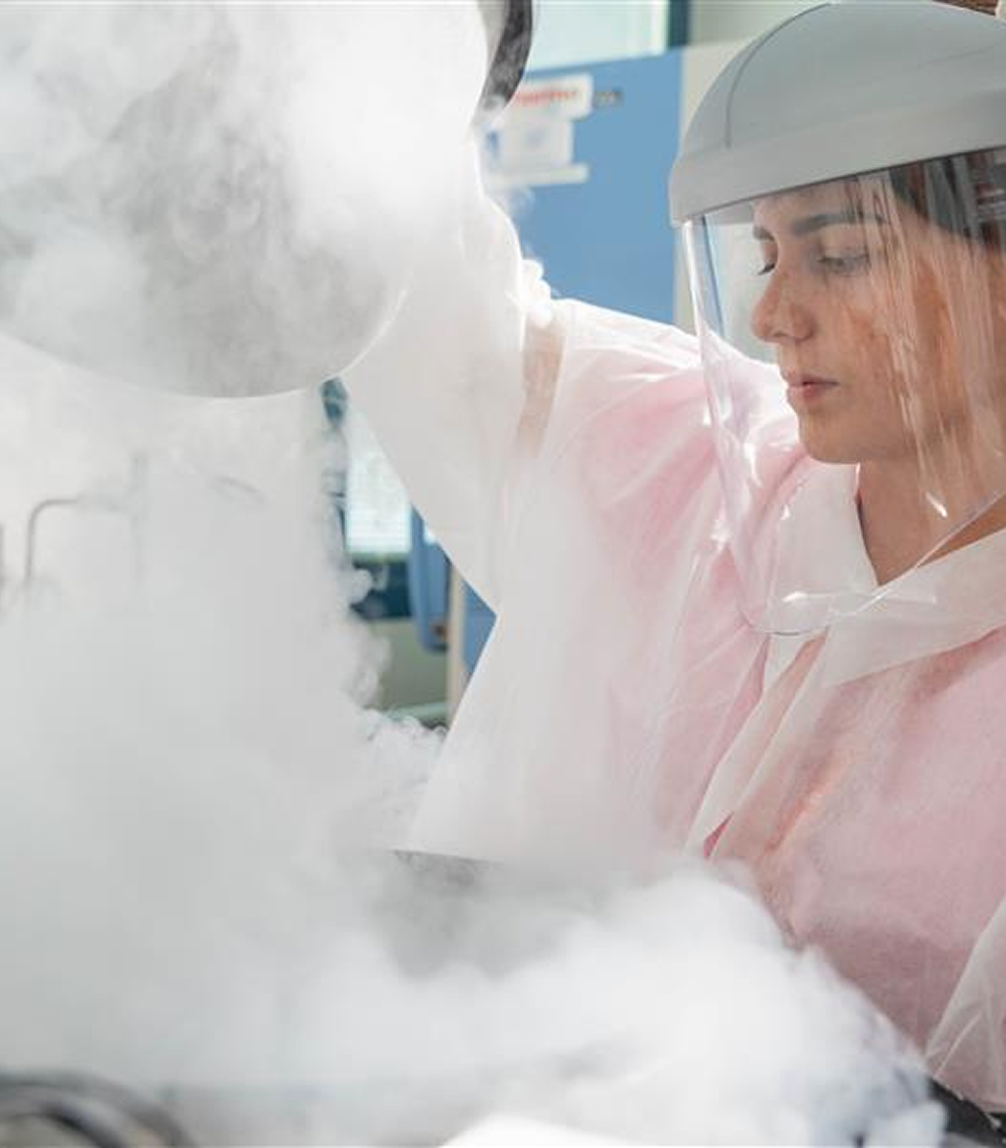
The entire production process spans several weeks and involves the expertise of highly specialized professionals, including biotechnologists and laboratory technicians.
Following purification, the active ingredient undergoes formulation, sterilization, and aseptic filling (Fill & Finish), which are carried out by selected external partners. The sterile product is then returned to Dompé for final labeling and packaging before being distributed globally.